
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example7 Bimetal under Thermal Load
General
-
A bimetal consisting of two different metal plates is analyzed.
It deforms when it is subjected to temperature change and thermal loaded.
-
The deformation, the displacement and the mechanical stress are solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
The temperature is applied evenly on the model.
Opt for the thermal load in the analysis condition, and set the reference temperature and the reached temperature.
There is no need to couple with the thermal analysis [Watt].
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solver |
Mechanical Stress Analysis [Galileo] |
|
Analysis Type |
Static analysis |
|
Options |
Select “Thermal load”. |
The Step/Thermal Load tab is set as follows.
|
Tabs |
Setting Item |
Settings |
|
Step/Thermal load |
Reference temperature |
25[deg] |
|
Step/Reached Temperature Setting |
Step 1: 60[deg] |
Model
Two flat solid bodies are created to form metal plates. One is copper and the other is tungsten. Their coefficients of expansion are different.
As it deforms itself, there is no need to set up the boundary conditions to constrain.
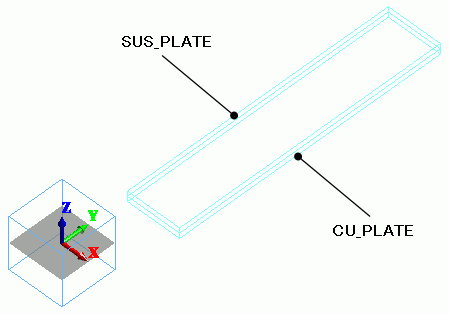
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Solid |
CU_PLATE |
008_Cu * |
|
1/Solid |
SUS_PLATE |
518_SUS410 * |
* Available from the Material DB
Boundary Conditions
N/A
Results
The contour indicates the displacement.
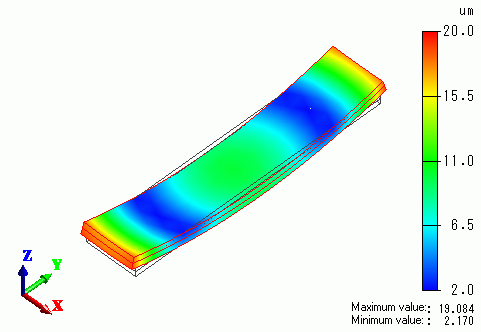
The copper expands more than the stainless steel when the temperature goes up.
As a result, the bimetal warps upward in the positive Z direction.
The vectors of the mechanical stress are shown below.
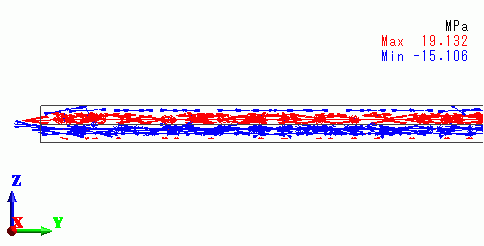
The upper plate is getting the tensile stress, whereas the lower plate is getting the compression stress.

