CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example18 Material with Anisotropic Elasticity
General
-
Rutile has the anisotropic elasticity. The deformation under pressure is solved.
-
The displacement and the mechanical stress are also solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solvers |
Mechanical Stress Analysis [Galileo] |
|
Analysis Type |
Static analysis |
|
Options |
N/A |
Model
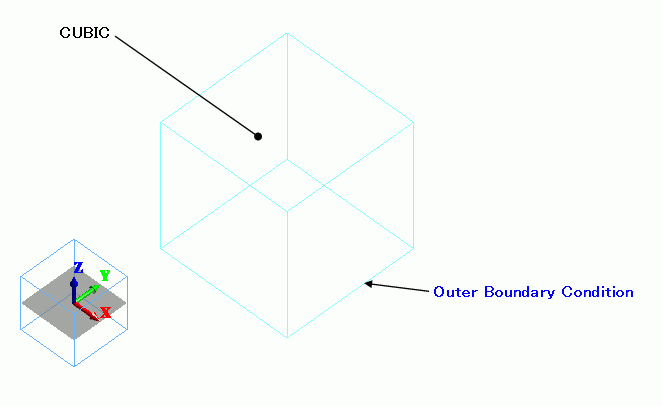
A cubic solid body is created. The material is rutile which has the anisotropic elasticity.
The anisotropic axis is oriented to (1, 1, 1), which is set on the direction tab of the body attribute.
The compressive pressure is set by the outer boundary condition.
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Solid |
CUBIC |
201_Rutile *
|
* Available from the Material DB
|
Body Attribute Name |
Direction |
|
CUBIC |
Specified by: Vector Vector: X=1.0, Y=1.0, Z=1.0 |
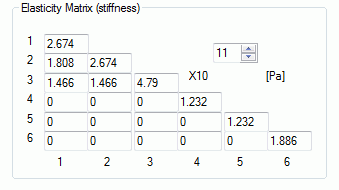
The matrix indicates that the 3-3 direction has the highest elasticity. Therefore, it is set to be (X, Y, Z)=(1, 1, 1).
Boundary Conditions
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
|
Outer Boundary Condition |
Mechanical |
Pressure |
1×10^6[Pa] |
Results
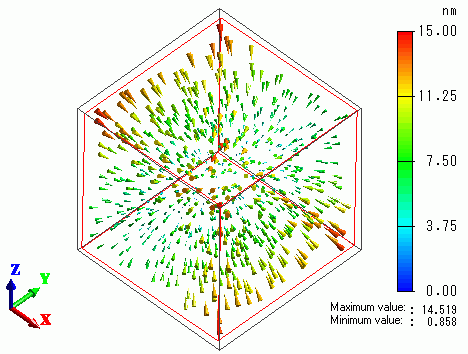
The vectors of displacement are shown below.
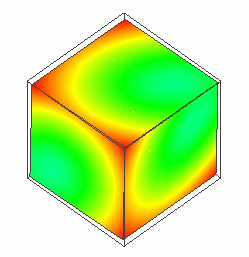
The displacement diagram is shown below. The contour diagram shows the displacement.
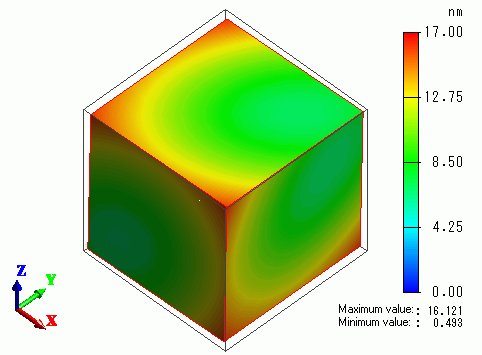
(X, Y, Z)=(1, 1, 1) exhibits the lowest compression displacement.
The vectors of internal mechanical stress are shown below.
The pressure is applied evenly, hence the internal stress is -1[MPa].