
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

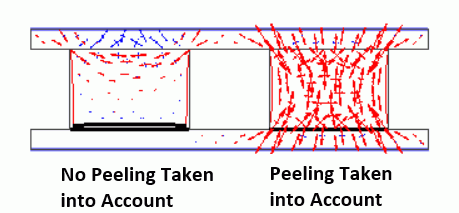
Example47 Peel Off
General
-
The “peel off”, one of the settings of the simple contact boundary condition, is studied in this exercise.
-
Two cubes are sandwiched by two plates. Both cubes are attached to the upper plate. The right cube is sticky and adheres to the lower plate. The left cube does not adhere to the lower plate at all. Their simple boundary conditions reflect the difference.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
2D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solvers |
Mechanical Stress Analysis [Galileo] |
|
Analysis Type |
Static analysis |
|
Options |
Select thermal load |
The Step/Thermal Load tab is set as follows.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Setting Item |
|||||||||||
|
Step/Thermal Load |
Step Setting |
Multi-step thermal load analysis |
|||||||||||
|
Reference temperature |
25[deg] |
||||||||||||
|
Step/Reached Temperature Setting |
|
Model
Two cubes are sandwiched by two plates. Both cubes are attached to the upper plate. The top face of the upper plate and the bottom face of the lower plate are fixed.
The right cube is sticky and adheres to the lower plate. The left cube does not adhere to the lower plate at all. Their simple boundary conditions reflects the difference.
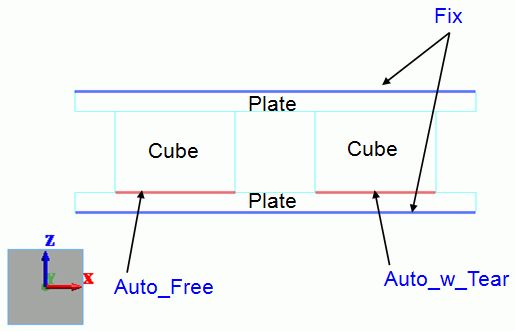
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Sheet Body |
Fixed_Plate |
Plate |
|
1/SheetBody |
Fixed_Plate |
Plate |
|
2/SheetBody |
Bond_Cube |
Cube |
|
3/SheetBody |
Bond_Cube |
Cube |
The material properties are set up as follows. The coefficient of expansion of the plates is set to zero.
|
Material Name |
Tab |
Properties |
|
Plate |
Elasticity |
Material Type: Elastic/Isotropic Young’s modulus: 1×10^9[Pa] Poisson’s ratio: 0.3 |
|
Coefficient of Expansion |
0.0 [1/deg] |
|
|
Cube |
Elasticity |
Material Type: Elastic/Isotropic Young’s modulus: 1×10^9[Pa] Poisson’s ratio: 0.3 |
|
Coefficient of Expansion |
10.0 [1/deg] |
Boundary Conditions
The boundary conditions set on the bottoms of the two cubes are different. See the table below for details.
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
|
Fix/Edge |
Mechanical |
Displacement |
Select the X and Z components. UX=0, UZ=0 |
|
Auto_Dry/Edge |
Mechanical |
Simple contact |
Simple contact classification : Automatic judgment |
|
Automatic judgment setting : Coefficient of friction : 0.0 Peel off taken into account : Deselected |
|||
|
Auto_Sticky/Edge
|
Mechanical |
Simple contact |
Simple contact classification : Automatic judgment |
|
Automatic judgment setting : Peel off taken into account : Selected Peel strength : 5×10^3[Pa] |
Results
The deformation and the maximum principal stresses (vectors) are shown below for each step.
< Step 1 / Reached temperature = 50 deg. >
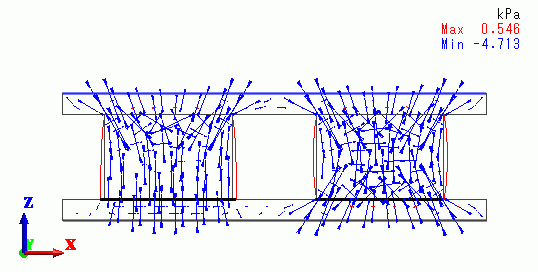 |
| Slip Bond |
The cubes expand due to the temperature rise.
The left cube slips on the lower plate and the right cube adheres to the lower plate.
< Step 2 / Reached temperature = 0 deg. >
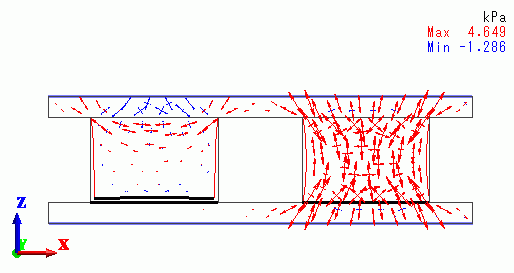 |
| Off contact Bond |
The cubes contract due to the descent of the temperature.
The left cube is off the lower plate. The right cube still adheres to the plate because the tensile stress on the boundary is less than the peel-off withstanding strength (5[kPa]).
< Step 3 / Reached temperature = -25 deg. >
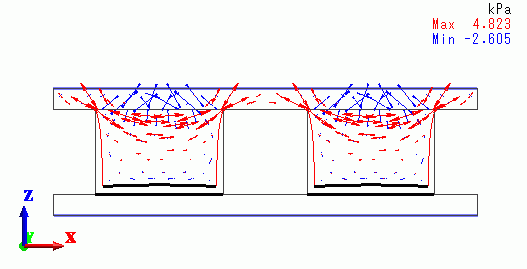 |
| Off contact Off contact |
Finally, the right cube is off the lower plate because the tensile stress exceeds the peel strength.

