
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example1 Acoustic Analysis of Tuning Fork
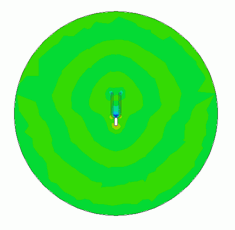
General
-
Acoustic analysis is performed on the model used in the stress-harmonic analysis Example 15.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Condition
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Solver |
Stress analysis [Galileo] Acoustic analysis [Mach] |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Analysis Type |
Harmonic Analysis |
|
Unit |
mm |
|
Analysis Options |
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Setting |
|
Harmonic Analysis |
Sweep Values |
Minimum: 500[Hz] Maximum: 2000[Hz] |
|
Sweep Type |
Linear step: Division number: 15 |
Model
The oscillation amplitude is set as a boundary condition on the face where the oscillation is forcibly applied.
The bottom face of the knob of the turning fork is where the oscillation is applied.
The air is set around the tuning fork.
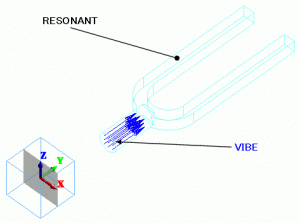
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
8/Solid |
RESONANT |
001_Al * |
|
10/Solid |
Air |
Air |
* Available from the material DB
Boundary Condition
In the harmonic analysis, the amplitude of the applied oscillation is set as the displacement amplitude in the boundary condition.
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Setting |
|
Oscillation/Face |
Mechanical |
Displacement |
Select the Y component. UY=1×10-5[m] |
|
Outer Boundary Condition |
Acoustic |
Open boundary |
|
The oscillation is applied in the Y direction at the bottom face of the knob. The amplitude is 10[um].
Results
The sound pressure at 2000Hz is shown below.
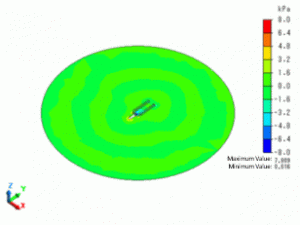
The sound wave is driven by the oscillation of the tuning fork.

