
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example9 Magnetization of IPM Motor
General
-
The magnetization of the IPM motor (interior permanent magnet motor) is analyzed.
The analysis takes the following two steps.
-
Magnetization Analysis
A magnetization current is applied to the magnet. -
Analysis Using Magnetization Results
The magnetization results give by step 1 are set to the magnet to analyze the motor torque.
-
The magnetization ratio, the magnetization distribution, the torque, and the magnetic flux density distribution are solved.
-
The homogenizing method is applied to simulate the layer structure of the electromagnetic plates of steel for the core.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
-
In this example, a quarter period symmetric model is used for faster calculation.
Show Results
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Analysis Space |
2D |
|
Thickness in Depth Direction |
60[mm] |
|
Unit |
mm |
|
Solver |
Magnetic Analysis [Luvens] |
|
Analysis Type |
Transient Analysis |
|
Options |
[Partial Model (Symmetric Model) Setting] Select Partial Model. Division number: 4 Select Convert the result to the full model for output |
Set the Mesh Tab as follows.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Setting |
|
Mesh |
Set the general mesh size automatically: Deselect General Mesh size: 1[mm] |
|
|
Automatic Ambient Air Creation |
Select Create ambient air automatically Ambient Air Scale: 1.2 |
The transient analysis tab is set as follows.
-
The intensity of the magnetic field is obtained for each timestep. At some timestep, the intensity drops. The magnetization field is determined by the intensity of the magnetic field at a timestep just before it drops.
The timestep setting does not affect the result as the constant current is used in this example.
The same result will be obtained if the timestep setting is switched to [steady-state analysis]. -
In order to take the induced current into account, input waveform has to be of the magnetization current instead of the constant current.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Setting |
|||||||
|
Transient Analysis |
Timestep |
Manual |
|||||||
|
Table |
|
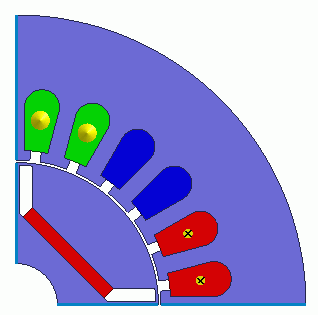
Model
A rotor core and magnet are placed in the center. A stator and coils are placed around them.
The motor has 4 poles and 24 slots.
The magnetization current is set to the coils I1,I2,I3, and I4.
This is a 2D model analysis.
By utilizing the symmetry, the model is quarter period symmetric.
Rotation period boundary (symmetric) is set.
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
12/Sheet |
Mag |
Magnetize_Mat |
|
11/Sheet |
Rotor |
35JN270_JFE Steel* |
|
28/Sheet |
Stator |
35JN270_JFE Steel* |
|
30/Sheet |
U1+ |
008_Cu * |
|
31/Sheet |
U1+ |
008_Cu * |
|
32/Sheet |
W1- |
008_Cu * |
|
33/Sheet |
W1- |
008_Cu * |
|
34/Sheet |
V1+ |
008_Cu * |
|
35/Sheet |
V1+ |
008_Cu * |
* Available from the material DB
The body attribute is set up as follows.
The magnetization current is set to the coils I1,I2,I3, and I4.
A variable [current] is used for easy modification.
For the core, the homogenizing method is selected to simulate the layered steel plates.
|
Body Attribute Name |
Tab |
Setting |
|
Mag |
Direction |
Vector: X=1, Y=0, Z=1 |
|
Current |
Click Yes for induced current setting. |
|
|
Rotor |
Layer |
Select Take layer into account Space: 97[%] Layer direction vector: X=0, Y=1, Z=0 |
|
Stator |
Layer |
Select Take layer into account Space: 97[%] Layer direction vector: X=0, Y=1, Z=0 |
|
I1, I2 |
Current |
Waveform: Constant Current value: current (using variable) Turns: 35[Turns] Direction: +Y direction |
|
I3, I4 |
Current |
Waveform: Constant Current value: current (using variable) Turns: 35[Turns] Direction: – Y direction |
|
I0 |
Current |
Waveform: Constant Current: 0[A] |
The material properties are set as follows.
The magnetization characteristics are defined. See Permeability tab for details of the parameters of the magnetization characteristics.
|
Material Name |
Tab |
Properties |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Magnetize_Mat |
Permeability |
Material type: Magnetizing material |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Initial Magnetization Characteristics B-H Curve Table
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Definition Type of Magnetization Rate: Normalize with coercivity Magnetization Ratio Table
Coercivity at magnetization ratio of 1.0: 980000[A/m] |
Boundary Condition
Half period symmetric boundary is set.
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Setting |
|
Symmetric |
Symmetry/Continuity |
Periodic |
Rotation Period (Half Period) |
Results
There are two steps of analysis as follows.
-
Magnetization Analysis
A magnetization current is applied to the magnet. -
Use Magnetization Result
The magnetization results give by step 1 are set to the magnet to analyze the motor torque.
The results of 1 are shown below. (The results of the analysis model [Magnetization analysis].)
The magnetization distribution with the magnetization current (variable “current”) of 100 to 1900 [A] is shown below.
The magnetization is almost fully achieved at 1900 [A].
|
100[A] |
700[A] |
1300[A] |
1900[A] |
The diagram below shows the magnetization distribution.
|
100[A] |
700[A] |
1300[A] |
1900[A] |
The analysis result of step 2 is shown below. (The results of the analysis model [Torque analysis (use magnetization results].)
In this analysis model, the result of step 1 is set to the magnet.
(Material type is set to [Use Magnetization Result] on the [Permeability] tab.)
The torque wave at the magnetization current of 1300 [A] is shown below.
The magnetic flux density at the magnetization current of 1300 [A] is shown below.

