
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example2 Directivity of Disc
General
-
A vibrating disc is placed in the air. The sound waves generated by it are analyzed.
-
The sound pressure levels are calculated for the points on the hemisphere, and the radiation patterns are solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model unit |
m |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solver |
Acoustic Analysis [Mach] |
|
Analysis Type |
Harmonic analysis |
|
Options |
N/A |
The harmonic analysis tab is set up as follows.
The sound waves propagate outside the analysis region. Therefore the “open boundary” condition below is applied initially.
|
Tabs |
Setting Item |
Settings |
|
Harmonic analysis
|
Frequency |
Minimum: 52.7[Hz] Maximum: 52.7*5[Hz] |
|
Sweep Type |
Select Linear step by division number. Division number: 2 |
|
|
Sweep Setting |
Select Fast sweep. Tolerance: 1.0×10^-2 |
|
|
Open Boundary Tab |
Type |
Absorbing boundary |
|
Order of Absorbing Boundary |
1st degree |
|
|
Coordinates of Origin |
x = y = z = 0 |
Model
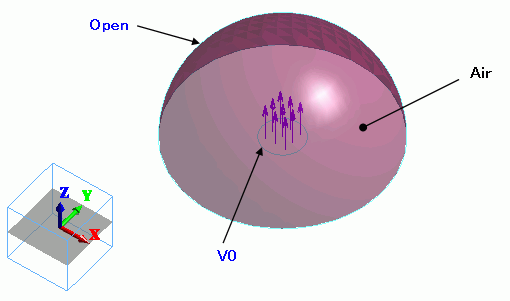
The air hemisphere is created from a solid body. The “open boundary” is set on the surface of the hemisphere.
The “speed” boundary condition is set on the circular face topology, which is created by segmenting the circular sheet body.
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Solid |
Air |
000_Air(*) |
* Available from the Material DB
Boundary Conditions
The “speed” boundary condition is set on the face of the imprinting body.
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
|
Open/Face |
Acoustic |
Open boundary |
|
|
V0/Face |
Acoustic |
Speed |
1[m/s] |
Results
The sound pressures at the points distanced 100 m away from the origin are solved and the directivities are shown below.
On the [Results] tab  , click ▼ at the side of
, click ▼ at the side of ![]() , and select Directivity.
, and select Directivity.
The [Directivity Calculation] dialog box will show up.
Set it up as follows, and press the Polar Graph button.
The directivity will be shown in polar graph for each frequency.
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Mode: Frequency [Hz] |
Select the mode to display. |
|
Observation Point |
r: 100[m] φ: Enter 0 in all θ: max 360[deg] step 100 |
|
Display |
Sound Pressure Level [dB] |
|
Plane of Symmetry |
XY plane |
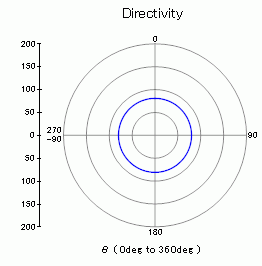
The polar graph of the sound pressure level at 52.7[Hz] The unit is [dB]
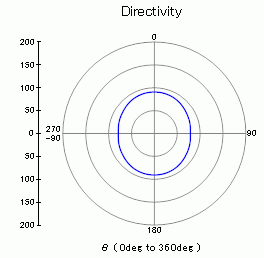
The polar graph of the sound pressure level at 158.1[Hz] The unit is [dB]
The polar graph of the sound pressure level at 263.5[Hz] The unit is [dB]
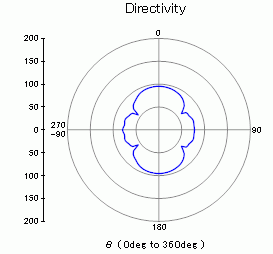
The sound pressure varies as the drive frequency changes.

