CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example4 Heating of Conductive Strip (Steady-State Analysis)
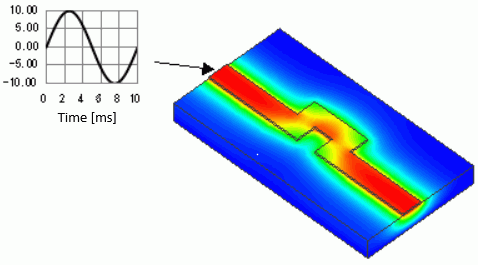
General
-
In this exercise, the AC voltage of 100Hz is applied for the same model as Exercise 2.
-
The steady state after a long lapsed time is calculated.
-
There are no changes in the other conditions.
Analysis Conditions
In this exercise, the AC voltage of 100Hz is applied.
The time step which is set in the transient analysis tab should be shorter than one eighth of the AC voltage period ( 10[ms] / 8).
The difference from Exercise 2 is indicated by red letters in the table.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Settings |
|
Transient analysis |
Time step |
Manual |
|
Restart |
Deselect |
|
|
Time step |
0.5^-3[s] |
|
|
Calculation steps |
20 |
Boundary Conditions
The difference from Exercise 2 is indicated by red letters in the following table.
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
|
T_Wall/Face |
Thermal |
Adiabatic |
|
|
T0/Face |
Thermal |
Temperature |
25[deg] |
|
V0/Face |
Electric |
Electric wall |
Waveform: Constant, Voltage: 0.00[V] |
|
V1/Face |
Electric |
Electric wall |
Waveform: Sine wave Frequency: 100Hz Voltage : Minimum -0.01V Voltage : Maxmum +0.01V |
|
Outer Boundary Condition * |
Thermal |
Heat Transfer/Ambient Radiation |
Heat transfer coefficient: 10 [W/m2/deg] Ambient temperature: 25[deg] |
Click Check Waveform button on “Electric wall” tab in the boundary condition setting dialog for V1,
and the applied voltage will show up in graph form.
Results
The temperature at (5.5, 3.5, 1.1) is shown below.