CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example37 Plastic Deformation due to Repetitive Displacement
General
-
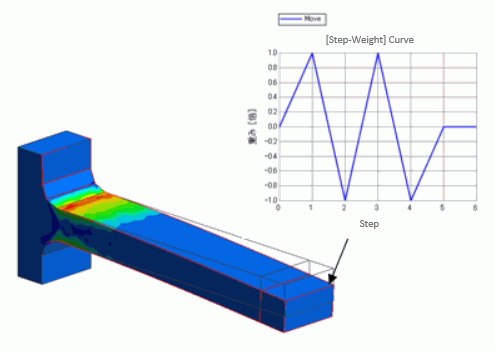
Repetitive displacement is applied on a tip of a bar.
-
Multi-steps are set up. Time dependency is given to the displacement boundary of the tip of the bar.
And repetitive displacement is set up.
-
The death of bodies can be processed with multi-step analysis.
The tip of the bar disappears at the last step. -
ON/OFF setting in the boundary condition will give the same results.
* Analysis model with ON/OFF set in the boundary condition is also included in the project file. -
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solver |
Mechanical Stress Analysis [Galileo] |
|
Analysis Type |
Static analysis |
|
Large deformation |
Select “Large displacement”. |
The Step/Thermal Load tab is set as follows.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Item |
|||||||||||||
|
Step/Thermal Load |
Step Setting |
Multiple steps |
|||||||||||||
|
Step/Reached Temperature Setting |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Options for the Multi-Step Analysis |
Save the results of substeps : Select |
The number of steps is 6. The number of substeps varies depending on the time-dependent weighting.
It is set to 10 on the substeps with the largest displacement.
By selecting “Save results of substeps”, the results at substeps can be output.
Model
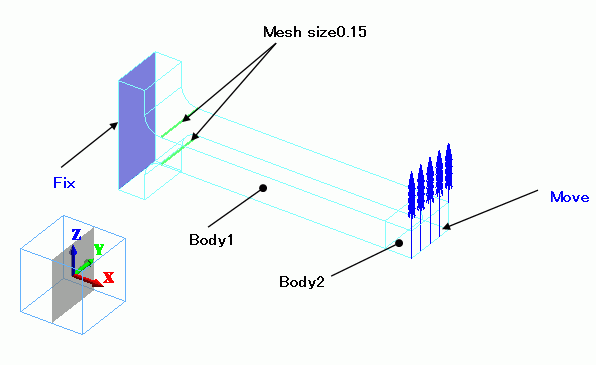
One end of the bar is fixed, while the other end is free and displaced repetitively.
The stress is concentrated at the fixed end. Therefore the finer mesh size is set around there.
The bar consists of two parts: One is the tip of the bar and the other is the main portion of the bar. The tip of the bar is to disappear at the last step.
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
2/Solid Body |
Body2 |
ElastoPlasticMaterial |
|
3/Solid Body |
Body1 |
ElastoPlasticMaterial |
The material properties are set up as follows:
|
Material Name |
Tab |
Properties |
|
ElastoPlasticMaterial |
Elasticity |
Material Type: Elasto-plastic/Bilinear Hardening Law: Isotropic hardening
Material Property: Young’s modulus 1×10^9[Pa] Poisson’s ratio 0.3 Strain hardening rate 0.05×10^9[Pa] Initial yield stress 4×10^6[Pa]
|
Body2 is to die at Step 6, which can be set on the Analysis Domain tab as follows.
|
Body Attribute Name |
Tab |
Settings |
|
Body2 |
Analysis Domain |
Death step: Step 6 |
Boundary Conditions
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
|
Fix/Face |
Mechanical |
Displacement |
Select all X/Y/Z components. UX=0, UY=0, UZ=0 |
|
Move/Face |
Mechanical |
Displacement |
Select the Z component. UZ=-0.25×10^-3[m]
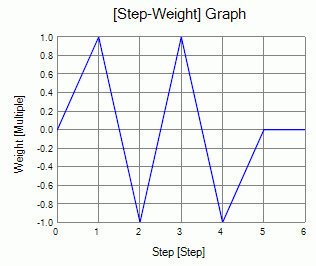
Select “Time dependency” and set the weight function as follows.
With the weight setting above, the displacement is forcibly applied for 2 cycles.
|
Results
The accumulated equivalent plastic strain at the final state which is step 6 is shown below.
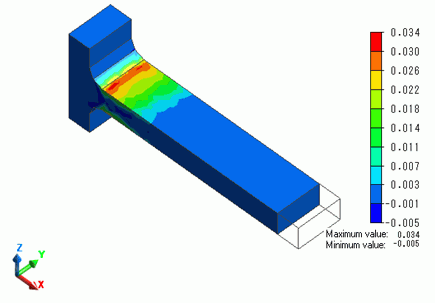
High strains are exhibited at the fixed end of the bar.
The accumulation of strains over time is clear as shown below. The horizontal axis is time.
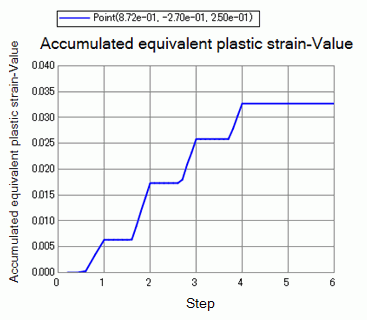
The plastic strains accumulate over time.
Distributions of the principal stresses at steps 5 and 6 are shown below.
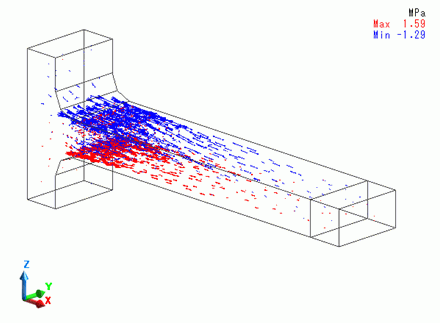
The principal stress at step 5
At the step 5, as the Z displacement at the tip of the bar has returned to 0 from minus direction, the top side is getting the compression force, while the bottom side is getting the tensile force.
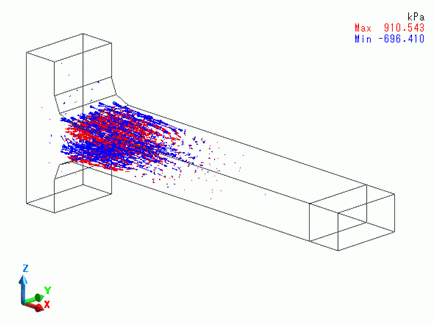
The principal stress at step 6
At step 6, the tip of the bar has disappeared. There are the residual stresses at the fixed end.