CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example23 Toroidal Coil
General
-
The magnetic field produced by a toroidal coil is analyzed.
-
The vectors of the magnetic field and the magnetic flux density are solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
-
******
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solvers |
Magnetic Field Analysis [Gauss] |
|
Analysis Type |
Static analysis |
|
Options |
N/A |
Set the Mesh Tab as follows.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Settings |
|
Mesh |
Meshing Setup |
Automatically set the general mesh size: Deselect General mesh size: 1[mm] |
Model
Coil (Cur) is wound on the ferrite core (Ferrite).
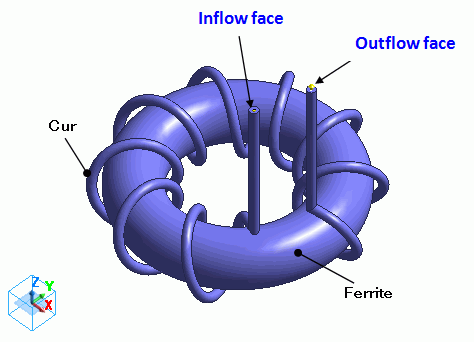
The coil’s form is given by the following equations.
x = ( A*sin(t*N) + B ) * cos(t)
y = ( A*sin(t*N) + B ) * sin(t)
z = A*cos(t*N)
A: The radius of the coil.
B: The distance from the center of the toroid to the center of the coil
N: The number of turns of the coil
t: Angle
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Solid |
Ferrite |
Ferrite |
|
5/Solid |
Cur |
008_Cu |
* Available from the Material DB
|
Material Name |
Tab |
Settings |
|
Ferrite |
Permeability |
Relative Permeability: 1×10^3 |
Boundary Conditions
No setting.
Results
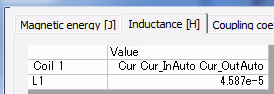
To see the calculation results of electromagnetic force and inductance, go to the [Results] tab

click [Table] ![]() .
.
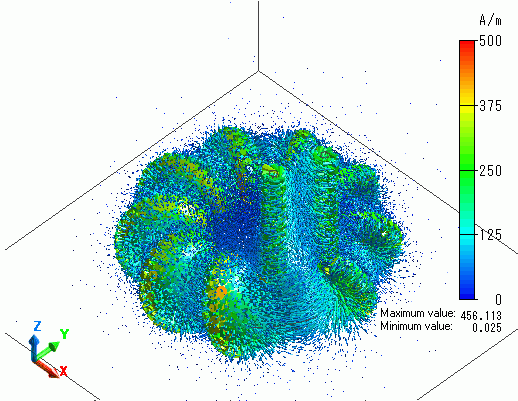
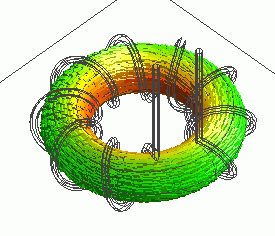
The vectors of the magnetic flux density are shown below.
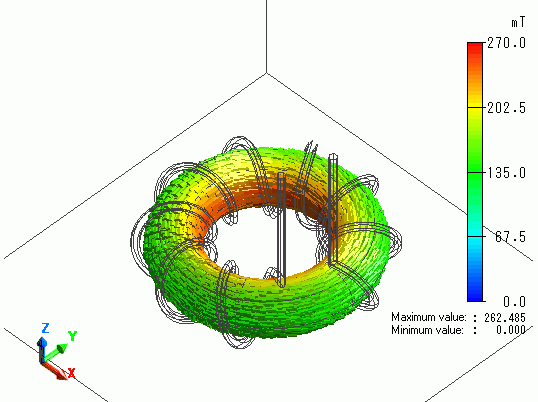
The vectors of the magnetic field are shown below.