
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example19 Resonant Frequency
General
-
Harmonic analysis is used in this Exercise while resonant analysis is used in Exercise 13.
-
Analysis with the initial stress taken into account is performed. See Analysis with the initial stress taken into account for the details.
-
The frequency characteristics of the displacement is solved.
-
Analysis 1: Apply the static load to the bar and pull it at both ends.
Analysis 2: Fix the bar at both ends. Vibrate it by applying the voltage. The displacement in the Analysis 1 is used to take into account the hardening effect of tensile force.
Analysis Space (Common to Analyses 1 and 2)
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions (Analysis 1)
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Solver |
Piezoelectric Analysis [Rayleigh] |
|
Analysis Type |
Static Analysis |
|
Options |
N/A |
Graphical Objects (Analysis 1)
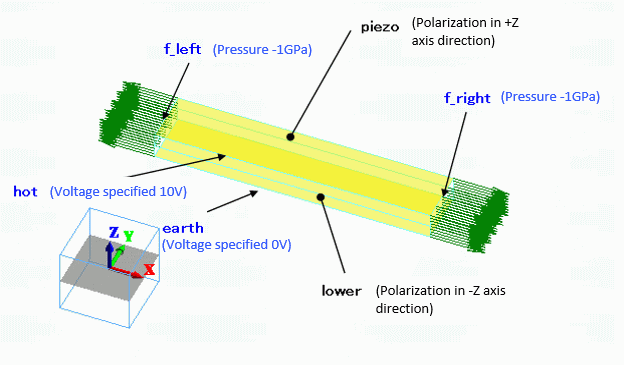
Two reversely polarized piezoelectric bars are stuck together. The ends are set with the “pressure” boundary condition. The top and bottom faces are set with the “voltage specified” boundary condition.
Body Attributes and Material properties Setting (Common to Analyses 1 and 2)
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Solid |
upper |
000_P-4 * |
|
1/Solid |
lower |
000_P-4 * |
(*) Available from the Material DB
The polarizations are set as follows.
|
Body Attribute Name |
Tab |
Setting |
|
upper |
Direction |
Specified by: Vector Vector: X=Y=0.0, Z=1.0 |
|
lower |
Direction |
Specified by: Vector Vector: X=Y=0.0, Z=-1.0 |
Boundary Conditions (Analysis 1)
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Setting |
|
earth/Face |
Electric |
Electric wall |
Voltage specified: Voltage 0[V] |
|
hot/Face |
Electric |
Electric wall |
Voltage specified: Voltage 10[V] |
|
f_left/Face |
Mechanical |
Pressure |
-1×10^9[Pa] |
|
f_right/Face |
Mechanical |
Pressure |
-1×10^9[Pa] |
Results (Analysis 1)
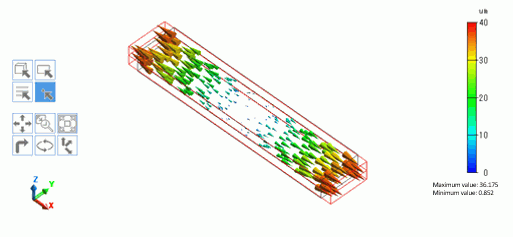
The bar is pulled at both ends. The vector diagram of the displacement is shown below.
Analysis Conditions (Analysis 2)
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Solver |
Piezoelectric Analysis [Rayleigh] |
|
Analysis Type |
Harmonic analysis |
|
Options |
Analysis with the initial stress taken into account Select Take into account. Select Use analysis result (Result import) |
The harmonic analysis tab is set up as follows.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Setting |
|
Harmonic Analysis |
Sweep Values |
Minimum: 35[KHz] Maximum: 50[KHz] |
|
Sweep Type |
Select “Linear step by division number”. Division number: 50 |
|
|
Sweep Setting |
Discrete sweep |
Result Import tab is set as follows.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Setting |
|
Result Import |
Specify Result |
For analysis model, |
Graphical Objects (Analysis 2)
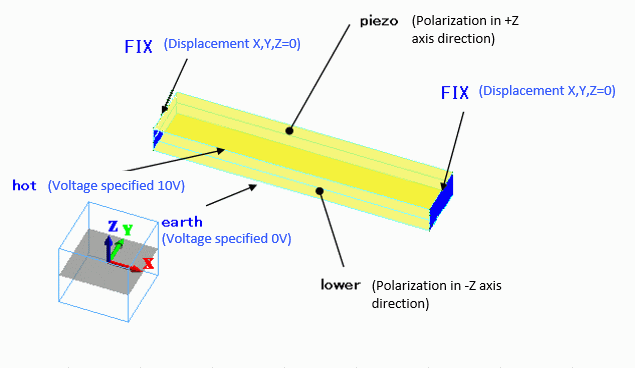
The analysis model is same as Analysis 1 (static analysis) except that both ends are fixed in Analysis 2.
Body Attributes and Material properties Setting (Analysis 2)
Same as Analysis 1.
Boundary Conditions (Analysis 2)
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Setting |
|
FIX/Face |
Mechanical |
Displacement |
Select all UX/UY/UZ components. X=Y=Z=0.0[mm]
|
|
earth/Face |
Electric |
Electric wall |
Voltage specified: Voltage 0[V] |
|
hot/Face |
Electric |
Electric wall |
Voltage specified: Voltage 10[V] |
Results (Analysis 2)
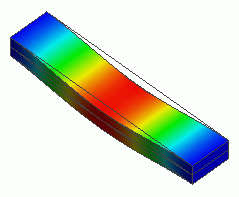
The frequency characteristics of displacement are solved by the analyses with and without the static load.
|
With static load/44.9KHz, Z displacement/Absolute |
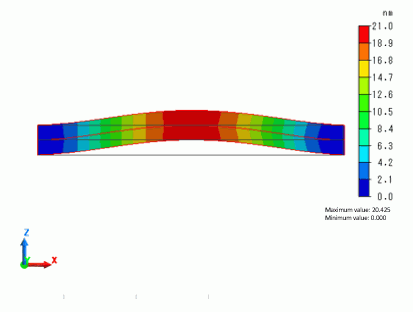 |
The contour above shows the displacement component Z absolute at the coordinates (5,1,0) near the resonant point in the analysis with static load.
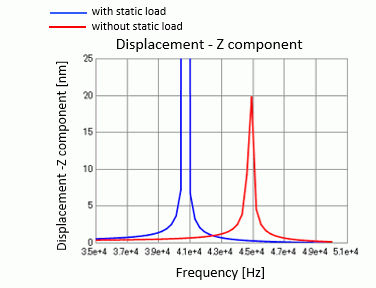
The peak shifted to the higher frequency due to the tensile force. This is the same effect as the Exercise 13 where it shifted to 4481[Hz] from 4070[Hz].

