
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example25 Periodic Boundary

General
-
The thermal analysis using the periodic boundaries is explained here.
-
The temperature distribution and the heat flux vectors are solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Solver |
Thermal analysis [Watt] |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Analysis Type |
Steady-state analysis |
|
Unit |
mm |
|
Analysis Options |
None |
Model

Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
Mesh Size |
|
0/Solid |
SUB |
006_Glass_epoxy *1 |
|
|
1/Solid |
GND |
008_Cu *1 |
|
|
2/Solid |
MAINCHIP |
001_Alumina *2 |
|
|
3/Solid |
SUBCHIP |
001_Alumina *2 |
|
|
4/Solid |
HOLE |
008_Cu *1 |
0.5 |
|
5/Solid |
HOLE |
008_Cu *1 |
0.5 |
|
6/Solid |
HOLE |
008_Cu *1 |
0.5 |
|
7/Solid |
HOLE |
008_Cu *1 |
0.5 |
|
8/Solid |
HOLE |
008_Cu *1 |
0.5 |
|
9/Solid |
HOLE |
008_Cu *1 |
0.5 |
|
10/Solid |
HOLE |
008_Cu *1 |
0.5 |
|
11/Solid |
HOLE |
008_Cu *1 |
0.5 |
*1 Available from the Material DB.
Boundary Condition
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Setting |
|
Outer Boundary Condition |
Thermal |
Heat transfer/Ambient radiation |
Natural convection (automatic calculation) Room temperature: 25[deg] |
|
t40 |
Thermal |
Temperature |
40[deg] |
|
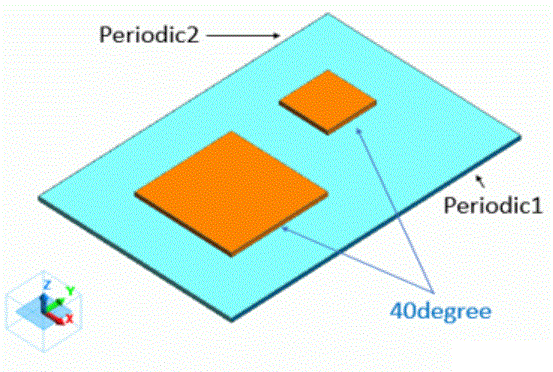
Periodic1 |
Symmetry/Continuity |
Periodic |
|
|
Periodic2 |
Symmetry/Continuity |
Periodic |
|

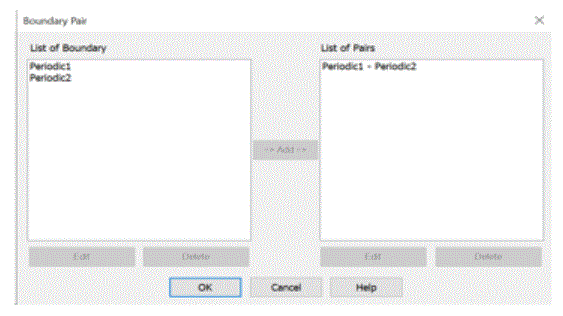
[Periodic1] and [Periodic2] are set periodic boundary pair.
Select “Natural convection (automatic calculation)” on the outer boundary condition.
* The correction coefficient for the natural convection is calculated automatically. See [Heat Transfer/Ambient Radiation] for more information.
Results
The temperature diagram is shown as below.

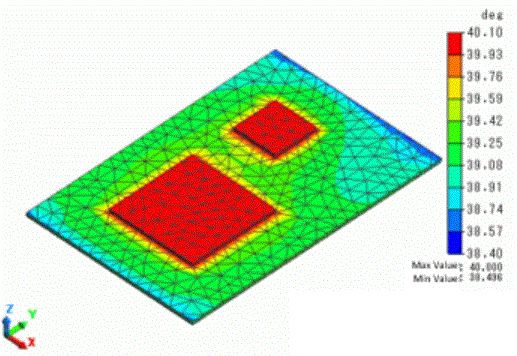
You can see the temperature is the same on the faces with periodic boundaries.

