
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example2 Turbulent Flow between Parallel Plates
General
-
The steady-state analysis is applied to the fluid which is flowing at the constant velocity between the parallel plates.
-
The fluid velocity distribution, the turbulent flow energy distribution, and the fluid velocity vectors are solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
-
Obtain this session's project file. (Save the project file before open)
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Analysis Space |
2D |
|
Model Unit |
mm |
Show Results
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Solver |
Fluid Analysis [Bernoulli] |
|
Analysis Type |
Steady-State Analysis |
|
Laminar Flow/Turbulent Flow |
Select Turbulent Flow |
|
Meshing Setup |
General Mesh size: 1[mm] |
Model
The material of Air (000_Air) is set to a rectangular sheet body. The boundary conditions of inlet and outlet are set on the left edge and the right edge respectively.
The solid wall outer boundary condition is automatically applied to the top and bottom edges where the boundary condition is not set.
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Solid |
pass |
000_Air(*) |
* Available from the material DB
Boundary Condition
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Setting |
|
Inlet/Edge |
Fluid |
Inlet |
Forced Inflow |
|
Outlet/Face |
Fluid |
Outlet |
Natural Outflow |
The Reynolds number calculated from this model form, material property, and fluid velocity is about 33104. The turbulent flow is analyzed as the number is large.
Generally, the laminar flow transitions to turbulent flow at the Reynolds number in the order of 1000.
Viscosity μ=1.82e-5[Pa s]
Density ρ: 1.205[kg/m3]
Kinematic viscosity v=μ/ρ=1.82e-5/1.205=1.510e-5[m2/s]
Fluid velocity V=50[m/s]
Distance between plates L=0.01[m]
Reynolds number Re = V*L/ν=50*0.01/1.510e-5 = 33104
Results
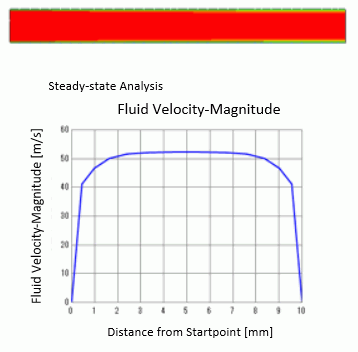
The distribution of the fluid velocities is shown below.
A graph below is given by selecting [Graph on edge] after right-clicking an edge near the outlet.
Unlike [Example 1 ] where the laminar flow is analyzed, the fluid velocity changes suddenly near the wall surface. The velocity is flat near the center.
The analysis result of K_turbulent flow energy is shown below.
The turbulent energy near the wall surface is high.

