CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example6 Cooling of IC by Natural Convection
General
-
Heat dissipation of an IC by the forced convection is solved by the steady-state analysis.
-
The temperature distribution and the heat flux vectors are solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions are applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model Unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Solver |
Fluid Analysis [Bernoulli] Thermal analysis [Watt] |
|
Analysis Type |
Fluid analysis: Steady-state analysis Thermal analysis: Steady-state analysis |
|
Laminar Flow/Turbulent Flow |
Select Turbulent Flow |
|
Options |
Select Take Buoyancy into Account (Natural Convection) |
|
Layer Mesh Setting for Wall Surface (General Settings) |
Parameters for Automatic Creation Expected Temperature Difference: 50[deg] |
|
Meshing Setup |
General Mesh size: 10 [mm] |
Model
The model is a box solid body. The material is Air (000_Air).
Set natural inflow/outflow to the outer boundary condition of Inlet/Outlet.
The substrate (VOL1) and IC (VOL2) are solid bodies.

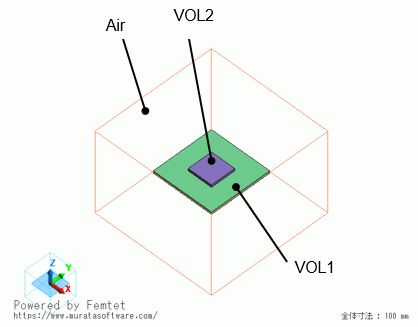
Setting of Body Attributes, Materials, and Mesh Sizes
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
Mesh Size |
|
0/Solid |
VOL1 |
006_Glass_epoxy * |
0.2 |
|
1/Solid |
VOL2 |
001_Alumina * |
0.2 |
|
2/Solid |
Air |
000_Air(*) |
– |
* Available from the material DB
IC (VOL2) is set as follows on the Heat source tab.
|
Body Attribute Name |
Tab |
Setting |
|
VOL2 |
Heat Source |
1W |
Boundary Condition
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Setting |
|
Outer Boundary Condition |
Fluid-Thermal |
Inlet/Outlet |
Natural Inflow/Outflow Inflow temperature: Use ambient temperature (25[deg]) |
Results
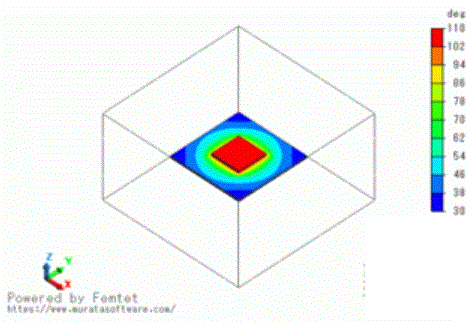
The temperature distribution is shown below.
For easy viewing of the temperature distributions of the substrate and the IC, the ambient air field is hidden by right-clicking the air body and selecting [Hide Body Field].
You can see the heat around the IC is higher than the other area.

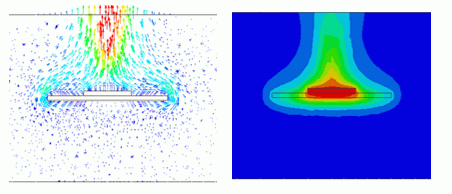
The cross section at x=0 is shown as below. The air body is shown as well.
There is a high-temperature area above the IC. It can be observed that the heat is transmitted mainly upward.

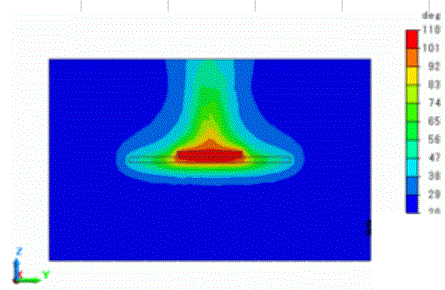
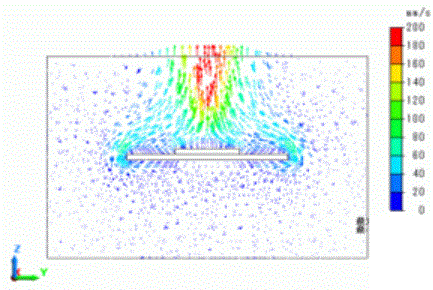
Next, switch the solver type from thermal to flud analysis. The flow velocity vectors are show as below.
In the graphics setup, the 3D vector is set OFF.
It is observed that the air heated by the IC is moving upward.