
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example16 Eddy Current Induced on Conductor Shell
General
-
External AC magnetic field is applied on a conductor shell . Eddy current on the shell is solved.
-
The vectors of the magnetic field and the magnetic flux density are also solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solver |
Magnetic Field Analysis [Gauss] |
|
Analysis Type |
Harmonic analysis |
|
Options |
N/A |
The frequency is set to 100[Hz] in the harmonic analysis tab. The external magnetic field is directing the Z direction.
Thus, the external magnetic field is set to be AC with the frequency of 100[Hz].
|
Tabs |
Setting Item |
Settings |
|
Mesh Tab |
Frequency-Dependent Meshing |
Surface treatment for conductors: None |
|
Harmonic analysis |
Frequency |
Minimum: 1×10^2[Hz] Maximum: 1×10^2[Hz] |
|
Step |
Linear step: Division number: 0 |
|
|
External magnetic field |
External magnetic field |
X=0, Y=0, Z=7.95774×10^5[A/m] (=1[Kgauss]) |
Model
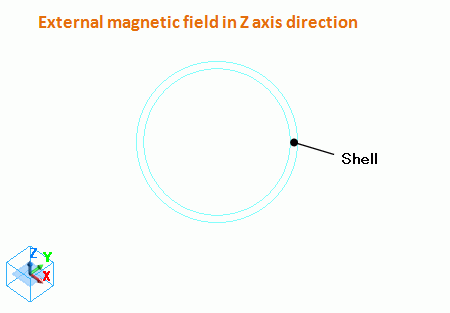
A spherical shell made of copper is placed and the external magnetic field is applied.
The magnetic field is AC as set in the harmonic analysis tab.
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
3/Solid |
Shell |
008_Cu * |
* Available from the Material DB
Boundary Conditions
When you set the external magnetic field, select magnetic wall as outer boundary condition.
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
|
Outer Boundary Condition |
Electric |
Magnetic wall |
|
Results
The current density on the shell surface is shown.
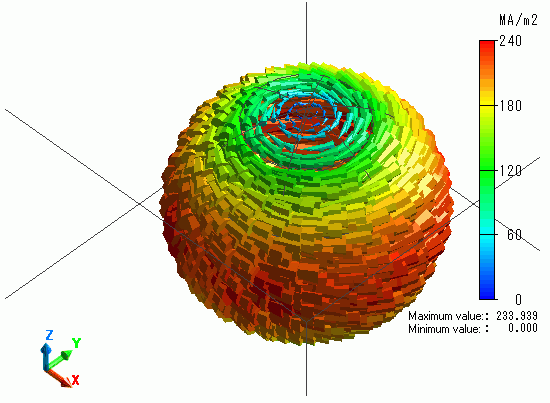
Eddy current is circulating around the Z axis.
The magnetic field sectioned at YZ plane is shown
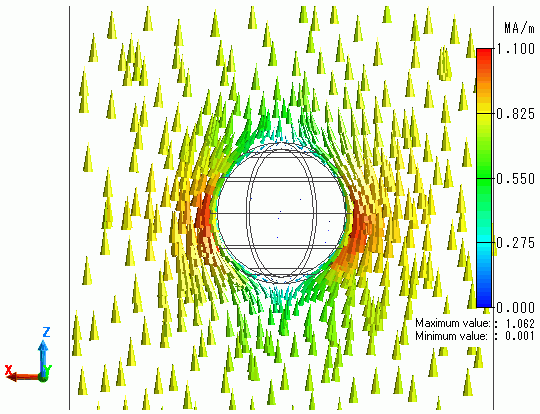
The magnetic field is distributed around the shell surface.
There is almost no penetration of the magnetic field into the shell.
The stronger the magnetic filed is, the larger eddy current is.

