
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example2 Circulator
General
-
A 3-port circulator consisting of a Y-shape waveguide and a ferrite cylinder is analyzed.
-
The device’s S-parameters are solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
-
[How to Reduce the Calculation Time]
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solver |
Electromagnetic Analysis [Hertz] |
|
Analysis Type |
Harmonic analysis |
|
Options |
Select “Ignore the influence of face/edge electrode thickness” * Field Data to Save: Don’t save |
* This is the default setting. There are no face electrodes with this model. Therefore it is irrelevant to select it or not.
The harmonic analysis is set up as follows.
|
Tabs |
Setting Item |
Settings |
|
Mesh Tab |
Element type |
2nd-order element |
|
Multigrid/Adaptive Mesh Method |
Select [Use the adaptive mesh method]. |
|
|
Frequency-Dependent Meshing |
Reference frequency: 10×10^9[Hz] Select “The conductor bodies thicker than the skin depth constitute the boundary condition.”
No conductive bodies are used in this session. However the setting above is required. |
|
|
Harmonic analysis |
Frequency |
Minimum: 0.8×10^10[Hz] Maximum: 1.2×10^10[Hz] |
|
Sweep Type |
Select Linear step by division number. Division number: 20 |
|
|
Input |
1.0[W} |
Model
The Y-shape waveguide is created by copying a solid body and uniting them with boolean operation.
The I/O Port boundary condition is set on their I/O faces.
The walls of the waveguide are defined as electric wall in the external boundary condition.
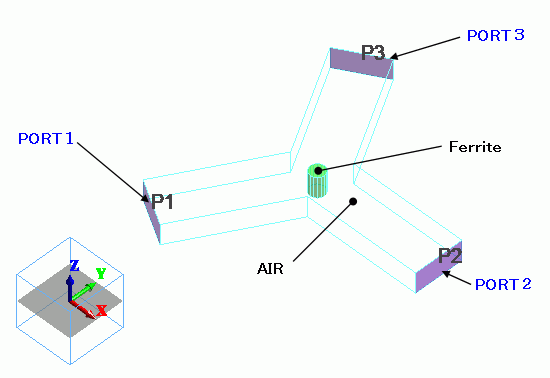
Body Attributes and Materials
The mesh size of the ferrite cylinder is set to 1.
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
Mesh Size |
|
3/Solid |
Air |
000_Air(*) |
1 |
|
4/Solid |
Ferrite |
Ferrite |
|
* Available from the Material DB
The static magnetic field applied on the ferrite (Ferrite) is set up in the body attribute.
|
Body Attribute Name |
Tab |
Material Name |
|
Ferrite |
Static Magnetic Field |
1.00×10^4[A/m] |
The material properties of Ferrite are set up as follows:
|
Material Name |
Tab |
Properties |
|
Ferrite |
Permittivity |
Relative permittivity: 1.1×10^1 |
|
Permeability |
Select “Use the tensor permeability”. |
|
|
Magnet |
Magnetization Strength: 1.3×10^-1
Properties of Ferrite: ⊿H: 7.958×10^3 [A/m] g coefficient: 2.0×10^0 |
Note) The following values are used for the magnet. Saturation magnetic flux density: 1300[Gauss], Magnetic resonance FWHM: 100[Oe],
Relative permittivity: 11, tanD: 0.0015. 1300[Gauss] = 0.13[T], 100[Oe] = 7958[A/m]
Boundary Conditions
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
|
PORT1/Face |
Electric |
I/O Port |
Reference Impedance: Select Number of Modes Number of precalculated modes: 5 Number of modes used in the actual analysis: 1 Select modes: none |
|
PORT2/Face |
Electric |
I/O Port |
Same as PORT1 |
|
PORT3/Face |
Electric |
I/O Port |
Same as PORT1 |
|
Outer Boundary Condition |
Electric |
Electric wall |
|
The outer boundary of Air:
The outer boundary of Air is set as the electric wall, which is the perfect conductor.
Results
Shown below is the I/O characteristics (S-parameters) between PORT1 and PORT2.
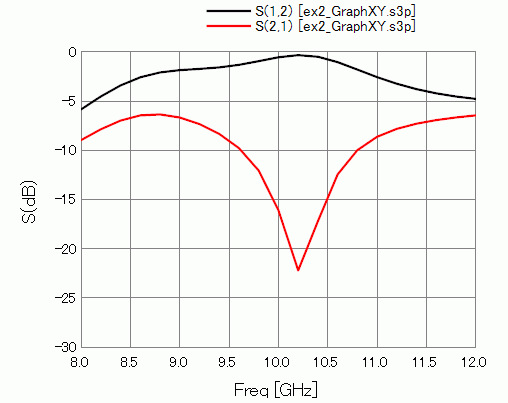
The isolation is exhibited around 10GHz.

