CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example14 Coaxial Cable
General
-
The characteristics of a coaxial cable are analyzed.
-
The propagation constant and the electromagnetic field distributions are solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
2D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solvers |
Electromagnetic Analysis [Hertz] |
|
Analysis Type |
Waveguide analysis |
|
Options |
Select “Ignore the influence of face/edge electrode thickness” * |
* This is the default setting. There are no face electrodes with this model. Therefore it is irrelevant to select it or not.
xx
The waveguide analysis is set as follows.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Settings |
|
Mesh Tab |
Element type |
2nd-order element |
|
Multigrid/Adaptive Mesh Method |
Select “Use the adaptive mesh method”. |
|
|
Frequency-Dependent Meshing |
Reference frequency: 1.0×10^9[Hz] Select “The conductor bodies thicker than the skin depth constitute the boundary condition.”
METAL is thicker than the skin depth. Its surface will be set with the proper boundary condition based on the material automatically. |
|
|
Waveguide analysis |
Analysis Type |
Propagation Constant Analysis |
|
Sweep Type |
Select Linear step Division number: 0 |
|
|
Propagation Constant Analysis |
Number of propagation modes: 1 Minimum frequency : 1×10^9[Hz] Maximum frequency : 1×10^9[Hz] |
Model
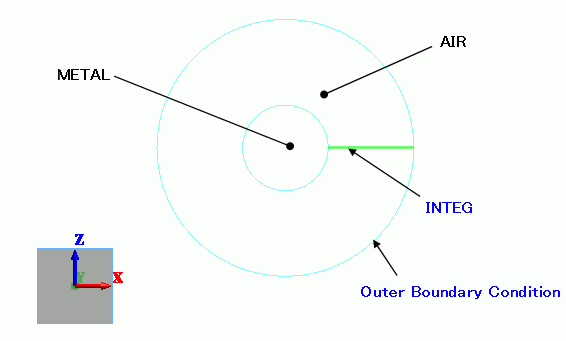
AIR and METAL are represented by circular sheet bodies.
The integral path is defined by a wire body. It is an imprinting body connecting the outer and inner perimeters of AIR.
The integral path is used for the calculations of potential differences and the characteristic impedances.
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Sheet |
METAL |
003_Ag * |
|
1/Sheet |
AIR |
000_Air(*) |
|
2/Wire |
Imprinting body |
|
* Available from the Material DB
Boundary Conditions
The outer boundary condition is set with the “Electric wall”.
The integral path is set with an imprinting body.
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
|
INTEG/Edge |
Electric |
Integral path |
|
|
Outer Boundary Condition |
Electric |
Electric wall |
|
Results
The calculation results are listed on the table.
The characteristic impedance is 66.3[Ω] and the phase constant is 21.0.
They are well matched with the theoretical values: Z0 = 65.9[Ω], β = 21.0
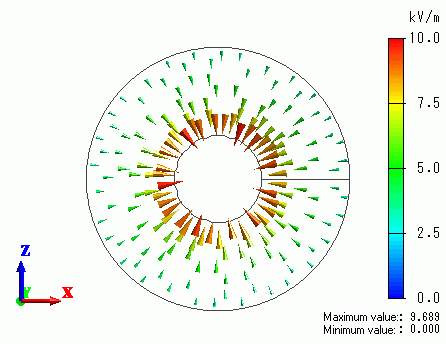
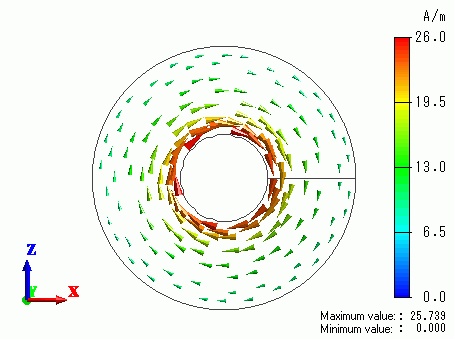
The electric and magnetic fields are shown below. The first figure shows the electric field vectors. The second figure shows the magnetic field vectors.