CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example23 Mixed-Mode S-Parameters Analysis of Balanced Line
General
-
The characteristics of a balanced line are analyzed.
-
The mixed-mode S-parameters are solved.
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Modelunit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
|
Item |
Setting |
|
Solver |
Electromagnetic Analysis [Hertz] |
|
Analysis Type |
Harmonic analysis |
|
Options for Electromagnetic Analysis |
Select Propagation mode transformation. |
Mesh, harmonic analysis, and open boundary are set as follows.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Setting |
|
Mesh |
Frequency-Dependent Meshing |
Reference frequency: 1×10^10[Hz] Select “The conductor bodies thicker than the skin depth constitute the boundary condition.” |
|
Harmonic Analysis |
Frequency |
Minimum: 0.1×10^9[Hz] Maximum: 5×10^9[Hz] |
|
Sweep Type |
Select Linear step by division number. Division number: 10 |
|
|
Sweep Setting |
Select discrete sweep |
|
|
Input |
1.0[W] |
|
|
Open Boundary |
Type |
Absorbing boundary |
|
Order of Absorbing Boundary |
1st degree |
Graphical Objects
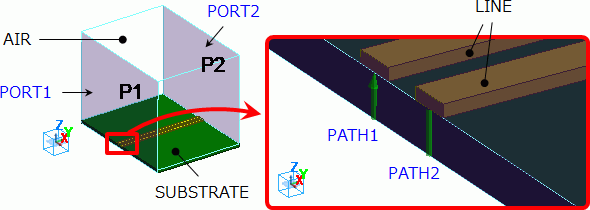
Two electrodes are created on a substrate. They function as a balanced line.
They are covered with rectangle air space.
Air and ports at both ends of the substrate are set as in the diagram below.
Set two integral paths (PATH1 and PATH2) connecting two electrodes and the bottom of the substrate.
The bottom of the substrate contacts the electric wall outer boundary condition.
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Solid |
SUBSTRATE |
006_Glass_epoxy * |
|
1/Solid |
AIR |
000_Air(*) |
|
2/Solid |
LINE |
003_Ag * |
|
3/Solid |
LINE |
003_Ag * |
|
5/Sheet |
Imprinting body |
|
|
6/Sheet |
Imprinting body |
|
(*) Available from the Material DB
Boundary Conditions
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Setting |
|
Port_001/Face |
Electric |
I/O Port |
Integral Path:
Reference Impedance:
Number of Modes
|
|
Port_002/Face |
Electric |
I/O Port |
Same as above. |
|
Outer Boundary Condition |
Electric |
Electric wall |
|
*1) Click [Differential pair] button while selecting PATH1 and PATH2.
The integral path in the same differential pair will be given the same number like “1” following the integral path name.
*2) Differential impedance can be selected if the differential pair is set.
Results
1. Propagation Mode
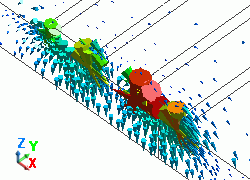
Select Port for [Analysis type]. From [Mode], select 5GHz which is the maximum analysis frequency.
As the number of modes to precalculate is set to 5,
five propagation modes are calculated for one frequency.
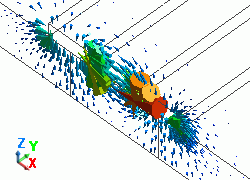
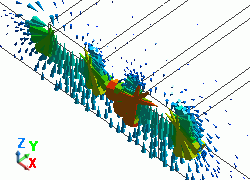
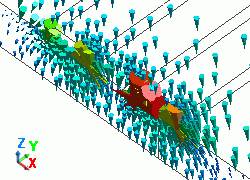
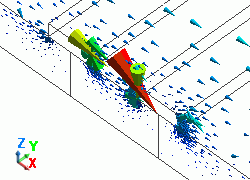
The diagram below shows the electric fields of five propagation modes calculated at PORT1 with 5GHz.
A part of the Propagation constant dialog box is also shown at the bottom of each picture in the diagram below.
Propagation constant dialog box can be opened from Mode Information of the [Chart] button.
|
Mode |
Differential Mode Analysis |
|
50: 5.000000e+09Hz: (0) |
PORT1 p1m1 |
|
51: 5.000000e+09Hz: (1) |
PORT1 p1m2 |
|
52: 5.000000e+09Hz: (2) |
PORT1 Not used |
|
53: 5.000000e+09Hz: (3) |
PORT1 Not used |
|
54: 5.000000e+09Hz: (4) |
PORT1 Not used |
You can tell that the differential mode is calculated first, and then the common mode is calculated at PORT1.
The third mode is not used in the 3D analysis as the Propagation constant dialog box shows “Not used”.
Please confirm that the differential and common modes are used in the 3D analysis also at PORT2.
2. S-Parameters
Click [SYZ Matrix] of the [Chart] button. SYZ Matrix dialog box will show up.
Select your desired component and click the [XY Graph] button.
Mixed-mode S-parameters graph will appear as in the diagram below.
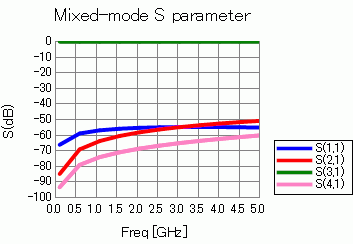
As shown in the Port Index of the SYZ Matrix dialog box, suffixes of S-parameters indicate the ports as follows.
|
Number |
Port: Mode |
|
1 |
PORT1:DIFF(PATH1,PATH2) |
|
2 |
PORT1:COM(PATH1,PATH2) |
|
3 |
PORT2:DIFF(PATH1,PATH2) |
|
4 |
PORT2:COM(PATH1,PATH2) |
“DIFF” means differential mode and “COM” means common mode.