
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example24 Waveguide-to-Coaxial Adapter
General
-
The characteristics of a waveguide-to-coaxial adapter are analyzed.
-
-
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Conditions
The harmonic analysis is set as follows.
|
Tab |
Setting Item |
Settings |
|
Mesh Tab |
Frequency-Dependent Meshing |
Reference frequency: 1×10^10[Hz] Select “The conductor bodies thicker than the skin depth constitute the boundary condition.”
|
|
Harmonic analysis |
Frequency |
Minimum: 8×10^9[Hz] Maximum: 15×10^9[Hz] |
|
Sweep Type |
Select Linear step Division number: 7 |
|
|
Sweep Setting |
Select Discrete sweep |
|
|
Input |
1.0[W] |
Model
The model is a waveguide-to-coaxial adapter. The inner conductor of coaxial cable is penetrated into the circular waveguide.
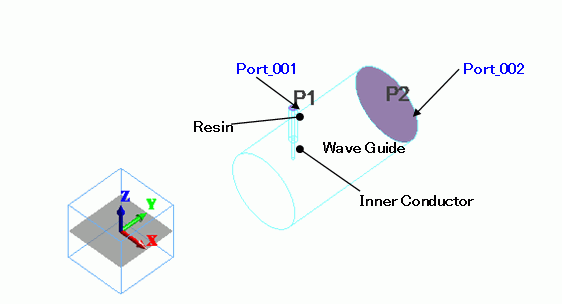
Body Attributes and Materials
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
7/Solid |
InnerConductor |
003_Ag * |
|
8/Solid |
Waveguide |
000_Air(*) |
|
9/Solid |
Resin |
Resin |
* Available from the Material DB
The material properties of Resin are set up as follows:
|
Material Name |
Tab |
Properties |
|
DRMat |
Permittivity |
Relative permittivity: 2.3
|
Boundary Conditions
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
|
Port_001/Face
|
Electric |
I/O Port
|
Reference Impedance: Select “Specify” and enter 50 ohms. Number of Modes Number of precalculated modes: 5 Number of modes used in the actual analysis: 1 Select modes: none |
|
Port_002/Face |
Electric |
I/O Port |
Reference Impedance: Select and enter 50[ohm]. Number of Modes Number of precalculated modes: 5 Number of modes used in the actual analysis: 2 Select modes: none |
|
Outer Boundary Condition |
Electric |
Electric wall |
|
Notes:
Number of modes used in the actual analysis is 2 for Port_002.
This is because there are two TE11 modes.
The directions of their electric field vectors are angled 90 degrees each other.
Both modes need to be taken into account for correct analysis. Femtet cannot control mode’s direction at the moment.
Results
Ports have been set as follows.
Port_001 Number of modes used in the actual analysis: 1
Port_002 Number of modes used in the actual analysis: 2
Therefore, S-parameters are a 3 x 3 matrix.
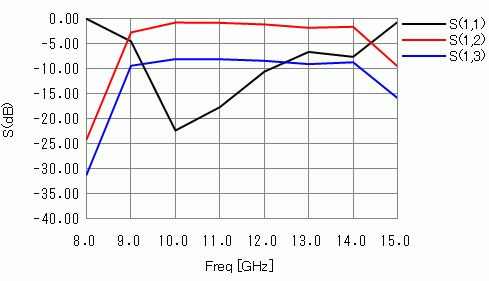
S-parameters
On the Results tab, click [Chart] – [SYZ Matrix]. The following will appear.
| Port Index |
| 1:Port_001:m1 |
| 2:Port_002:m1 |
| 3:Port_002:m2 |
“m1” and “m2” indicate the mode number.
See [How to Examine the Ports of Electromagnetic Analysis] for the detail.
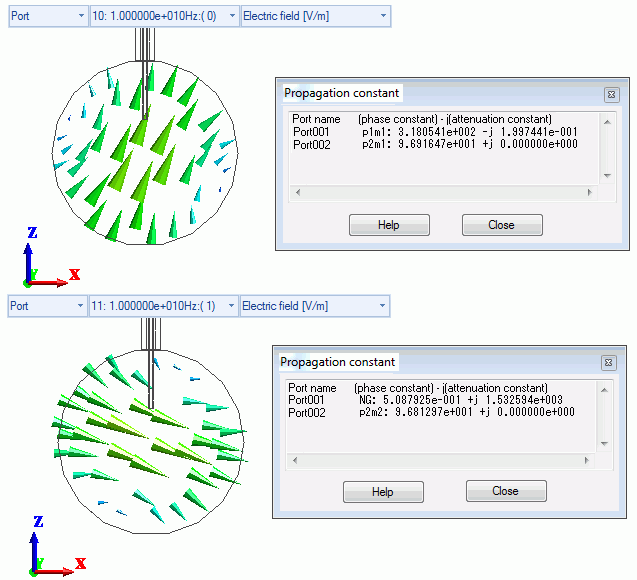
Two TE11 modes
The first propagation constant dialog box above shows the following:
(This dialog box appears when you click [Chart] – [Mode Information] on the Results tab  )
)
Port_002 p2m1: 9.691647e+001 +j 0.000000e+000
This is for Port_002:m1 of Port Index.
Note that “p” is for port and “m” is for mode in p2m1. The second “propagation constant” dialog box shows the following:
Port_002 p2m2: 9.681297e+001 +j 0.000000e+000
This is for Port_002:m2 of Port Index.
The power entered at Port_001 reaches Port_002 in these two modes.
The total power is acquired by the following equation.
Please use Excel or any other tool to calculate it. Femtet doesn’t calculate this equation.
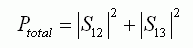 (1)
(1)
A TM01 mode also exists at 12[GHz] or higher. For better accuracy at 12[GHz] or higher,
increase “Number of modes used in the actual analysis” for Port_002 from 2 to 3.
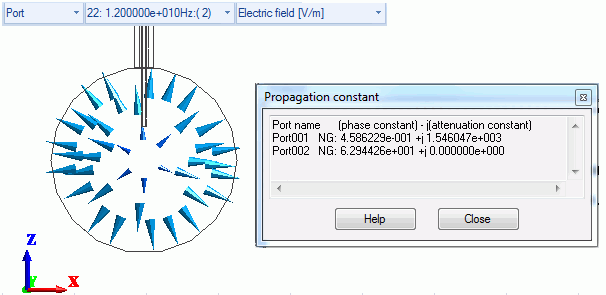
The TM0-mode electric field distribution (at 12GHz)

