
CAE Software【Femtet】Murata Software Co., Ltd.

Example8 Electroplating(Hull Cell Test Bath)
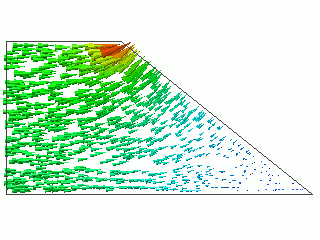
General
-
The electric field in the electroplating solution is analyzed.
-
The overvoltage at anode and cathode is taken into account.
The current density in the bath and the distribution of plating thickness are solved. -
Unless specified in the list below, the default conditions will be applied.
Analysis Space
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Analysis Space |
3D |
|
Model unit |
mm |
Analysis Conditions
The material is conductor for the plating analysis.
Select the [Perform the plating analysis] option.
|
Item |
Settings |
|
Solvers |
Electric Field Analysis [Coulomb] |
|
Analysis Type |
Static analysis |
|
Materials |
Conductor |
|
Options |
Select Perform the plating analysis |
Graphical Objects
The plating bath (Hull cell bath) is a solid body. The material is the plating solution.
The electrodes are set with the plating wall boundary condition.
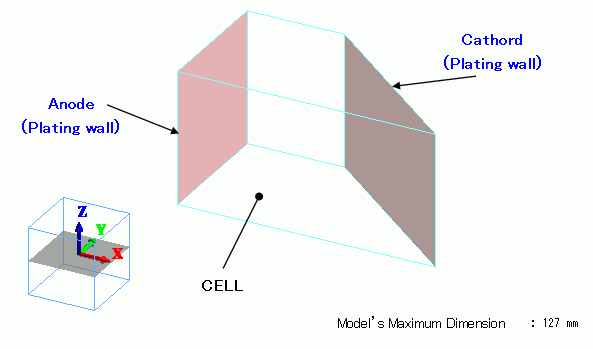
Body Attributes and Materials
The plating bath (Hull cell bath) is a solid body. The material is the plating solution.
|
Body Number/Type |
Body Attribute Name |
Material Name |
|
0/Solid |
Cell |
Plating Solution |
The body attribute of the plating solution is set as follows.
|
Body Attribute Name |
Plating Tab |
|
Cell |
Type of Plating Body: Plating Solution |
The conductivity of the plating solution is set as follows.
|
Material Name |
Conductivity Tab |
|
Plating Solution |
Conductivity Type: Conductor Conductivity: 10 [S/m] |
Boundary Condition
The boundary conditions are set as follows.
|
Boundary Condition Name/Topology |
Tab |
Boundary Condition Type |
Settings |
||||||||||||||
|
Cathode/Face |
Electric |
Plating wall |
Electrode Setting: Cathode
Overvoltage Type: Tafel’s Law
|
||||||||||||||
|
Anode/Face |
Electric |
Plating wall |
Electrode Setting: Anode
Overvoltage Type: Linear
Plating Condition: Current: 1.0[A] |
||||||||||||||
-
In this Exercise, Current is selected for the plating condition of the plating wall to perform analysis with specified current of the anode.
To perform analysis with specified voltage of the anode, select Voltage for the plating condition.
Calculations of the voltage-specified analysis is less than that of current-specified analysis, and the analysis time will be shorter.
Results
The current density vector is shown in Figure 1 below.
The current density distribution typical of the test bath is observed around the cathode.
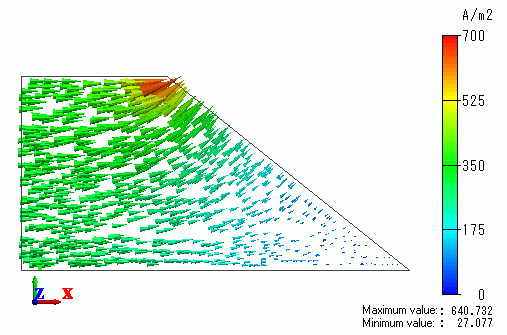
Figure 1 The current density vector
By using the drawing feature of Femtet, show the plating thickness extracted on the cathode.
Figure 2 shows the plating thickness along the cathode from the start point at the right bottom up to the right top.
Plating thickness is distributed according to the current density.
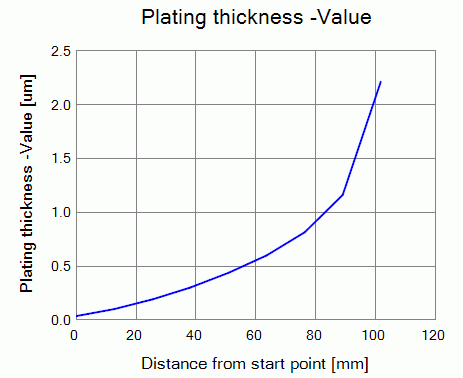
Figure 2 Distribution of the plating thickness
-
Refer to Field Graph for the detail of graph drawing.
(*) “Hull cell” is a product of YAMAMOTO-MS Co., Ltd.

